Liposomal vs Reduced Glutathione: Which Wins?
Table of Contents
Glutathione is an essential antioxidant that helps combat various health issues ranging from chronic diseases to skin problems. However, the question arises, which form of glutathione should you choose: liposomal or reduced? Both have their own set of benefits and drawbacks.
In this blog post, we will dive deep into understanding glutathione's role in the body and take a closer look at both liposomal and reduced glutathione. We will also compare them to help you make an informed decision on which one is best for you. Lastly, we will cover dosage recommendations for both forms and discuss any potential side effects associated with them. So let's get started!
What is Glutathione?
Glutathione is a vital antioxidant that plays a crucial role in our overall health. It helps combat oxidative stress and supports the body in various ways. One of its primary functions is detoxification, as it helps remove harmful toxins from the body. This is particularly important considering the modern-day exposure to environmental pollutants and toxins.
In addition to its detoxification properties, glutathione also plays a significant role in cellular processes. It is involved in DNA synthesis and repair, which is essential for maintaining the integrity and stability of our genetic material. Furthermore, glutathione is also known to support the function of the immune system, promoting a healthy and robust defense against pathogens.

Glutathione and Its Role in the Body
Glutathione, an essential antioxidant, plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy immune system. It acts as a key player in reducing inflammation and oxidative damage, helping to protect the body from harmful free radicals. Additionally, glutathione supports liver function by aiding in the detoxification of harmful substances, allowing the liver to effectively eliminate toxins from the body.
As we age or experience certain health conditions, our body's natural production of glutathione can decline. This decline in glutathione levels may have implications for overall health and well-being, as adequate levels of this antioxidant are essential for optimal cellular function.
In order to support glutathione levels, some individuals may choose to supplement with liposomal or reduced glutathione. Liposomal glutathione refers to a form of glutathione that is encapsulated within liposomes, which are tiny spheres made up of phospholipids. This delivery method is thought to enhance the absorption and bioavailability of glutathione.
On the other hand, reduced glutathione refers to the active form of glutathione that is naturally produced in the body. It is often administered in its reduced form to ensure maximum potency and effectiveness.
Both liposomal and reduced glutathione have their benefits and potential applications. However, it is important to note that the choice between the two forms ultimately depends on individual needs and preferences. Factors such as bioavailability, dosage recommendations, and potential side effects should be considered when deciding which form of glutathione to incorporate into a wellness routine.
What is Liposomal Glutathione?
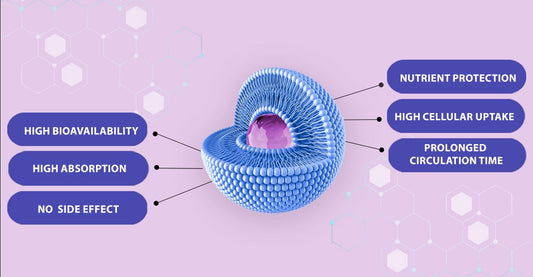
Liposomal glutathione is a specialized form of glutathione that offers enhanced absorption and bioavailability. This means that when you take liposomal glutathione, your body is able to absorb and utilize more of this important antioxidant.
- One of the key advantages of liposomal glutathione is its unique delivery system. The liposomes, which are tiny lipid spheres, protect the glutathione from degradation in the digestive system. This allows for a higher percentage of the glutathione to reach its target tissues, ensuring that you get the maximum benefit from this powerful antioxidant.
- Another benefit of liposomal glutathione is its sustained-release properties. Liposomal formulations provide a slow and steady release of glutathione into the bloodstream, maintaining optimal levels over an extended period of time. This is particularly important because glutathione is quickly metabolized in the body, and a steady supply is needed to support its many functions.
For individuals looking to optimize their glutathione levels, liposomal glutathione can be an ideal option. Whether you're dealing with chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, or simply want to support your overall health, liposomal glutathione can help. It provides a convenient and effective way to increase your glutathione levels and reap the benefits of this important antioxidant.
Top Benefits of Liposomal Glutathione
Liposomal glutathione is a specialized form of the antioxidant glutathione, which is essential for the proper functioning of the body. Liposomal delivery enhances the absorption and bioavailability of glutathione, leading to various potential benefits. While individual responses may vary, here are some of the top benefits associated with liposomal glutathione supplementation:
- Powerful Antioxidant Activity:
- Cellular Protection: Glutathione is a key antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals. Liposomal glutathione can enhance these protective effects due to its higher absorption rate.
- Detoxification Support:
- Liver Health: Glutathione plays a crucial role in the detoxification processes in the liver. By neutralizing toxins, it supports overall liver function and promotes the elimination of harmful substances from the body.
- Heavy Metal Detoxification: Glutathione is involved in binding to heavy metals and facilitating their excretion from the body, which can be especially beneficial for individuals with heavy metal toxicity.
- Immune System Support:
- Enhanced Immune Response: Glutathione supports the immune system by optimizing the function of immune cells. It helps in the proliferation and activity of lymphocytes and protects immune cells from damage, thereby enhancing the body's ability to fight infections and diseases.
- Anti-Aging Effects:
- Skin Health: Glutathione is known to promote healthy skin by preventing oxidative damage and supporting the repair of damaged tissues. This can contribute to a more youthful appearance.
- Cellular Longevity: By protecting cells from damage and supporting optimal cellular function, glutathione may have anti-aging effects at the cellular level.
- Neurological Health:
- Brain Protection: Glutathione is found in high concentrations in the brain and is essential for protecting neurons from oxidative stress. This antioxidant activity may help in reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases and supporting overall brain health.
- Respiratory Health:
- Asthma and Allergies: Some studies suggest that glutathione supplementation can help in managing symptoms related to respiratory conditions, such as asthma and allergies, by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the respiratory system.
- Energy Production:
- Mitochondrial Function: Glutathione supports mitochondrial function, which is vital for energy production in cells. By optimizing energy metabolism, it may contribute to increased energy levels and reduced fatigue.
- Support During Chronic Illness:
- Chronic Conditions: Glutathione supplementation, especially in liposomal form, is often used as a supportive therapy for various chronic illnesses, such as chronic fatigue syndrome, Lyme disease, and autoimmune disorders, due to its potential to modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation.
It's important to note that while liposomal glutathione offers enhanced absorption, individual responses to supplementation can vary. It's advisable to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to determine the appropriate dosage and assess potential interactions with existing medications or health conditions.

Liposomal vs Reduced Glutathione: The Comparison
Liposomal Glutathione and Reduced Glutathione are two different forms of the same antioxidant compound, glutathione. They are used for various health purposes, but they have some differences in terms of absorption, bioavailability, and potential uses. Here's a comparison of the two:
- Form:
- Reduced Glutathione (GSH): This is the active form of glutathione, the body's natural antioxidant. It consists of three amino acids: cysteine, glycine, and glutamic acid.
- Liposomal Glutathione: Liposomal glutathione is GSH encapsulated within lipid molecules called liposomes. This encapsulation is done to improve its absorption and bioavailability.
- Absorption and Bioavailability:
- Reduced Glutathione (GSH): Oral supplementation with GSH has poor bioavailability because it is broken down in the digestive system, and the absorption rate is limited.
- Liposomal Glutathione: Liposomal formulations are designed to protect GSH from degradation in the digestive system and increase its absorption in the bloodstream. This can potentially result in higher bioavailability compared to regular GSH supplements.
- Administration:
- Reduced Glutathione (GSH): It is available in various forms, including oral capsules, tablets, and intravenous (IV) administration.
- Liposomal Glutathione: Typically available as an oral supplement in liquid form.
- Uses:
- Reduced Glutathione (GSH): GSH plays a crucial role in detoxification processes in the body, supports the immune system, and acts as an antioxidant to help combat oxidative stress. It is used for various health conditions, including liver support, immune system enhancement, and as a general antioxidant.
- Liposomal Glutathione: Liposomal GSH is often marketed as having superior absorption, making it a popular choice for individuals seeking the potential benefits of GSH. It is used for similar purposes as GSH, such as antioxidant support and immune system health.
- Cost:
- Reduced Glutathione (GSH): Typically less expensive than liposomal formulations.
- Liposomal Glutathione: Liposomal supplements tend to be more expensive due to the specialized technology used in their production.
- Availability:
- Reduced Glutathione (GSH): More widely available in various forms and brands.
- Liposomal Glutathione: Less common and may not be available in all locations or from all suppliers.
- Considerations:
- If you are considering using glutathione for specific health concerns or as part of a treatment plan, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate form and dosage for your individual needs.
- Keep in mind that the efficacy of liposomal glutathione compared to traditional GSH supplements may vary depending on the individual and the specific health condition being addressed.
Liposomal glutathione is formulated to potentially enhance the absorption and bioavailability of glutathione compared to reduced glutathione supplements. However, the choice between the two depends on individual preferences, budget, and health goals. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs.
How Does the Body Absorb These Different Forms?
Different forms of glutathione are absorbed differently by the body. Liposomal glutathione is directly absorbed into the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system. On the other hand, reduced glutathione is broken down during digestion and absorbed as individual components. The liposomal delivery system protects glutathione from degradation, ensuring higher levels reach target tissues. Absorption efficiency may vary between liposomal and reduced glutathione.
What Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Liposomal and Reduced Glutathione?
When choosing between liposomal and reduced glutathione, it's important to consider personal goals and preferences. Liposomal glutathione offers enhanced absorption and bioavailability, while reduced glutathione is a natural and active form. Consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended to determine the best option considering factors like cost, convenience, and potential medication interactions.
Is There a Clear Winner Between Liposomal and Reduced Glutathione?
When it comes to liposomal and reduced glutathione, there is no clear winner. Both forms offer unique benefits and have their own advantages and disadvantages. The choice between liposomal and reduced glutathione depends on individual needs and preferences. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional before deciding which form is best for you.
Do Both Forms of Glutathione Have Side Effects?
Both liposomal and reduced glutathione typically have minimal side effects. Some people may experience mild digestive discomfort, so it's important to follow recommended dosages. If you have concerns, consult a healthcare professional. Proper storage and handling can also help maintain the effectiveness of glutathione supplements.
Let’s Sum Up
In conclusion, both Liposomal and Reduced Glutathione offer unique advantages and benefits. Liposomal Glutathione provides enhanced absorption and bioavailability, making it suitable for individuals with digestive issues. On the other hand, Reduced Glutathione is a more traditional form that supports the body's natural production of glutathione.
When choosing between the two, it’s important to consider factors such as individual health needs, preferences, and budget. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine the best option for you. Remember, maintaining optimal levels of glutathione is essential for overall health and well-being.